The design of optically active architectures based on gold nanoclusters (AuNCs) has gained considerable popularity in recent years. These architectures constitute a new class of ultra-small particles (<3 nm) known for their photoluminescence, photostability and high biocompatibility.
DNA engineering uses self-assembly processes to create perfectly defined architectures with sub-nanometre precision, which are excellent scaffolds for the construction of AuNC-based nanomaterials.
As part of this collaborative project, researchers took on the challenge of combining DNA fragments with AuNCs with fully controlled stoichiometry. To do this, they developed ligand engineering and controlled DNA functionalisation for nanoclusters of defined sizes, enabling them to construct one-dimensional (1D) assemblies of nanoclusters as well as three-dimensional (3D) architectures. Their characterisation, combining a set of analytical, structural and optical approaches, demonstrated high reproducibility and assembly efficiency for these superstructures.
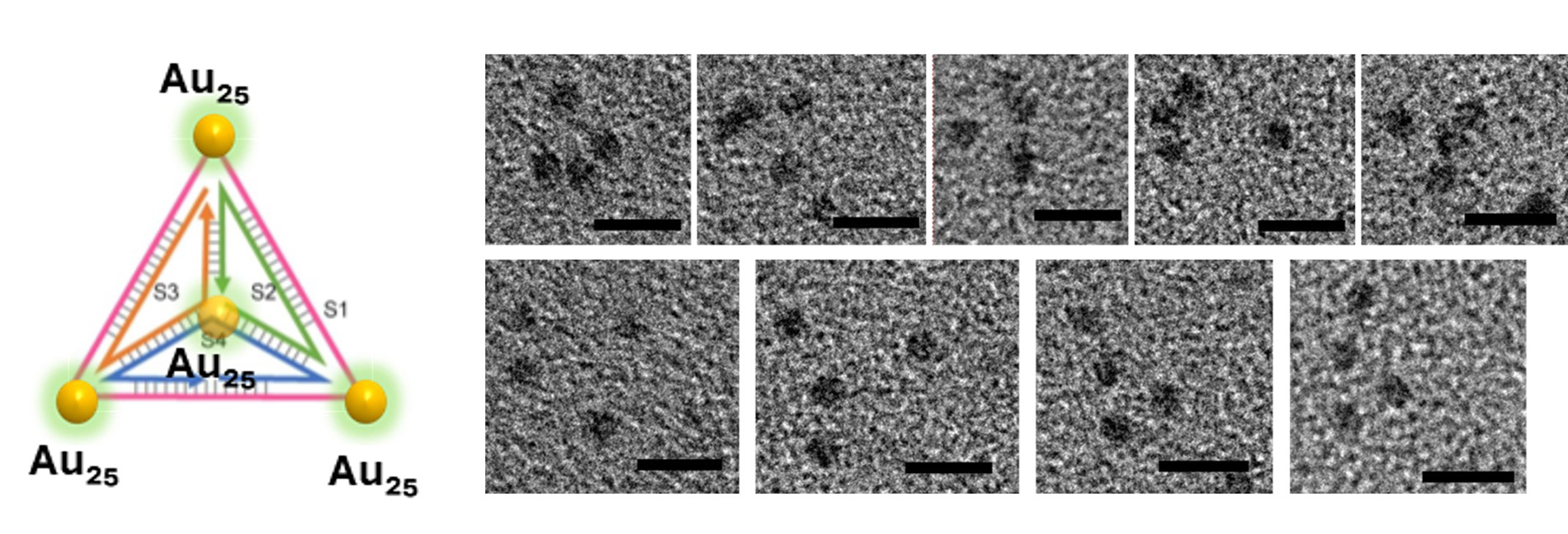
Figure : (A) Schematic representation of a DNA tetrahedron functionalised by four gold nanoclusters at its vertices. (B) Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) images of hybrid DNA-nanocluster tetrahedral nanostructures (scale = 5 nm). © CEA-Irig/SyMMES/D. Gasparutto
This work establishes a fundamental synthetic and analytical basis for the high-yield, high-purity preparation of defined multidimensional photonic nanoarchitectures. These biohybrid platforms offer particularly interesting prospects for their application as novel
theranostic agents*.
photonic nanomaterials*: materials with dimensions close to the wavelengths of visible light that interact with it.
theranostic agents*: molecules or nanomaterials used for imaging (diagnostics) and/or therapy (therapeutics).
UMR :
SyMMES, UMR 5819 CEA / UGA / CNRS / Grenoble-INP - UGA
Fundings :
UGA (CBH-EUR), ANR, Labex Arcane et Labex Gral, CEA-PTC
Collaborations :
Institut de Biologie Structurale (IBS), CEA-Irig
Institut de Biologie Avancée de Grenoble (IAB)