The regulation of gene expression by microRNAs* (miRNAs) is a major field of research in biology and medicine. These small non-coding molecules finely control protein production, and their deregulation is implicated in numerous pathologies. However, understanding their precise mode of action remains a scientific challenge.
In a study published in Nature Communications 2025, a CEA-IRIG/Biosante team has conducted a new critical analysis of pioneering data published in 2019. While these initial analyses concluded that several abundant miRNAs regulated the expression of a large number of their targets, the researchers demonstrate that this was an artifact linked to methodological biases.
By applying a systemic strategy and publicly sharing their analysis codes, they show that:
- only one miRNA, miR-92a-3p, shows robust anti-correlation with many predicted target genes,
- the majority of miRNAs, including highly expressed ones, do not exert a detectable generalized effect,
- the choice of analysis parameters (expression thresholds, evolutionary conservation of targets, prediction scores) influences results, and must therefore be standardized.
Beyond this critical review, the work establishes best practices for the exploitation of single-cell co-sequencing data. It stresses the need to assess the quality of target prediction software and experimental methods, and suggests using these data as reference tools to improve bioinformatics algorithms.
These advances reinforce the reliability of the conclusions that can be drawn from single-cell co-sequencing, a rapidly expanding technology. They will contribute to a better understanding of the role of miRNAs in complex diseases, and open up prospects for personalized medicine, where miRNAs are emerging as promising biomarkers and therapeutic levers.
This work confers on the team a recognized and rare competence in the analysis of co-sequencing datasets at the single-cell level, reinforcing its position as a reference in this emerging field.
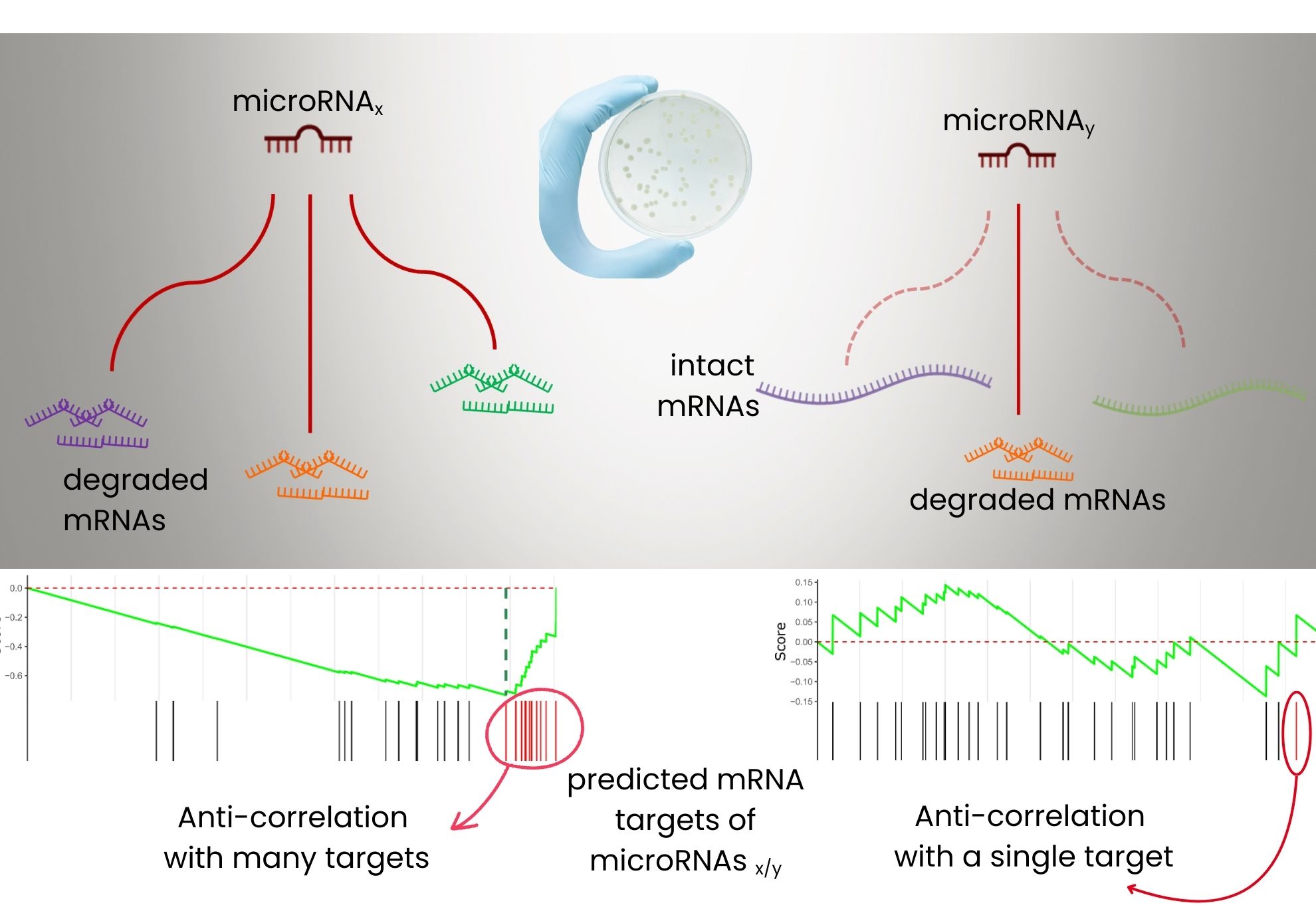
Statistical analysis of Single-Cell co-sequencing of microRNA-mRNA: Left, a microRNA degrading multiple mRNA targets, predicted both by an algorithm and by strong anticorrelation of expression. Right, a microRNA acting on a single target only, highlighting the diversity of regulatory mechanisms.
MicroRNAs* play a key role in regulating gene expression by degrading one or several messenger RNA (mRNA) targets. Yet, precisely identifying their modes of action remains a challenge, as their effects are often subtle and context-dependent. Single-cell co-sequencing, which simultaneously measures microRNA and mRNA expression in each cell, provides a unique and physiological way to explore these interactions.