Wallpass
An ultrasonic system that can transmit power and data through metal walls
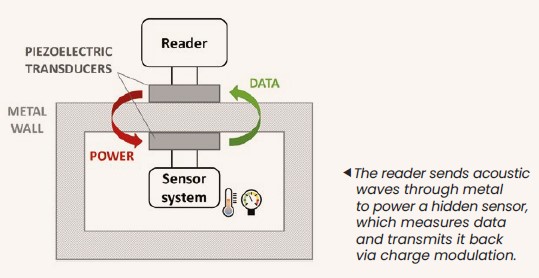
CEA-Leti's WallPass leverages an ultrasonic link between two coupled piezoelectric transducers to both charge and communicate with isolated sensors through metallic walls. In contrast to RFID and NFC technologies, WallPass takes advantage of acoustic waves that can transmit power and data through conductive materials such as metal.
With WallPass, temperature, pressure, strain, vibration, and other sensors placed inside enclosed metal environments like pipes and tanks can be powered and their data collected wirelessly. Wherever metal is a barrier to power and communication, CEA-Leti’s WallPass technology enables autonomous sensing.
What it can do
WallPass has been developed and validated for hard-to-access, isolated, and severe environments where making holes to route cables is either impractical or impossible:
- Metal pipes and tubes for oil & gas, geothermal, drilling, and fluid transportation,
- Bioproduction and vacuum tanks,
- Industrial machinery, motors, gearboxes, etc.,
- Nuclear reactor walls, submarine hulls.
WallPass can also transmit power and data through glass, ceramics, and hard plastics. Today, WallPass is also tested for transmitting power and data in the human body enabling autonomous, communicating medical prosthetics and implants.
|
What makes it unique
CEA-Leti's WallPass enables autonomous sensing through conductive materials like metal, even in high-temperature, high-pressure, and other hazardous environments. No wiring or batteries are required. In addition to transmitting data and power through a single acoustic channel with high efficiency, the technology developed by CEA-Leti is designed to be robust to fluctuating temperatures. It can also accommodate misaligned transducers by implementing acoustic beamforming by using multiple electrodes, and optimize the acoustic link using stacked transducers. There is currently no standard solution available on the market comparable to WallPass.
|