The particle transport in Tripoli-4 ® is performed in continuous-energy. The necessary nuclear data, i.e., cross-sections, scattering kernels, secondary energy-angle distributions, secondary particle yields, fission spectra, and so on, are read by Tripoli-4® from any evaluation written in ENDF-6 [1] format, including (but not limited to) JEFF, ENDF/B, JENDL and FENDL libraries. Tripoli-4® can directly access files in ENDF and PENDF format.
Tripoli-4® uses three separate files per simulated nuclide. The first is the ENDF file (i.e., the evaluation file), the second is the PENDF file created with NJOY [2] for the reconstructed Doppler-broadened cross-section. The third is the ANISO file that is produced by Tripoli-4 ® and contains specific data for the outgoing neutron. If the original anisotropy description is provided in terms of Legendre polynomials, Tripoli-4 ® converts it to equi-probable cosine bins before writing it into the ANISO file.
The probability tables for Tripoli-4 ® for the unresolved resonance range (URR), when present and requested, are generated by using the CALENDF code [3], and given in a fourth file. CALENDF first converts resolved and unresolved resonance parameters into temperature-dependent continuous-energy cross-sections. Then, the code generates on a user-specified energy grid cross-section probability tables, based on Gauss quadrature, which represent those cross-sections. Tripoli-4 ® uses these tables in the unresolved resonance range for each nucleus and the probability tables supersede the continuous-energy cross-sections available in the original PENDF file.
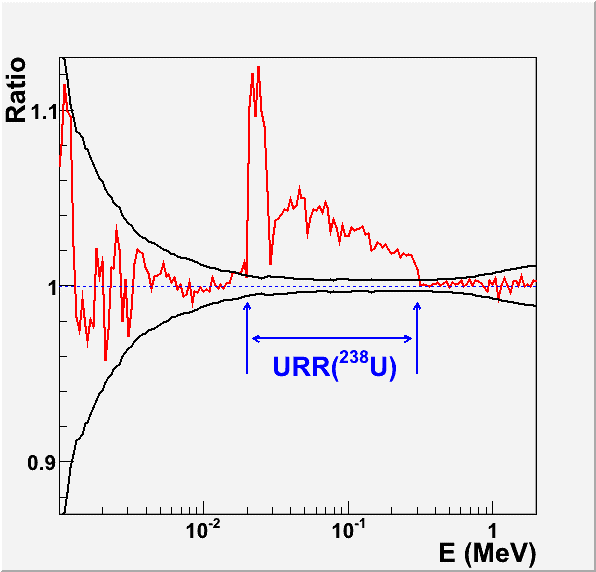
Ratio of neutron fluxes computed with and without probability tables for the IMF-012 benchmark.